Stereo Event-based Particle Tracking Velocimetry for 3D Fluid Flow Reconstruction
Yuanhao Wang, Ramzi Idoughi, Wolfgang HeidrichECCV, 2020
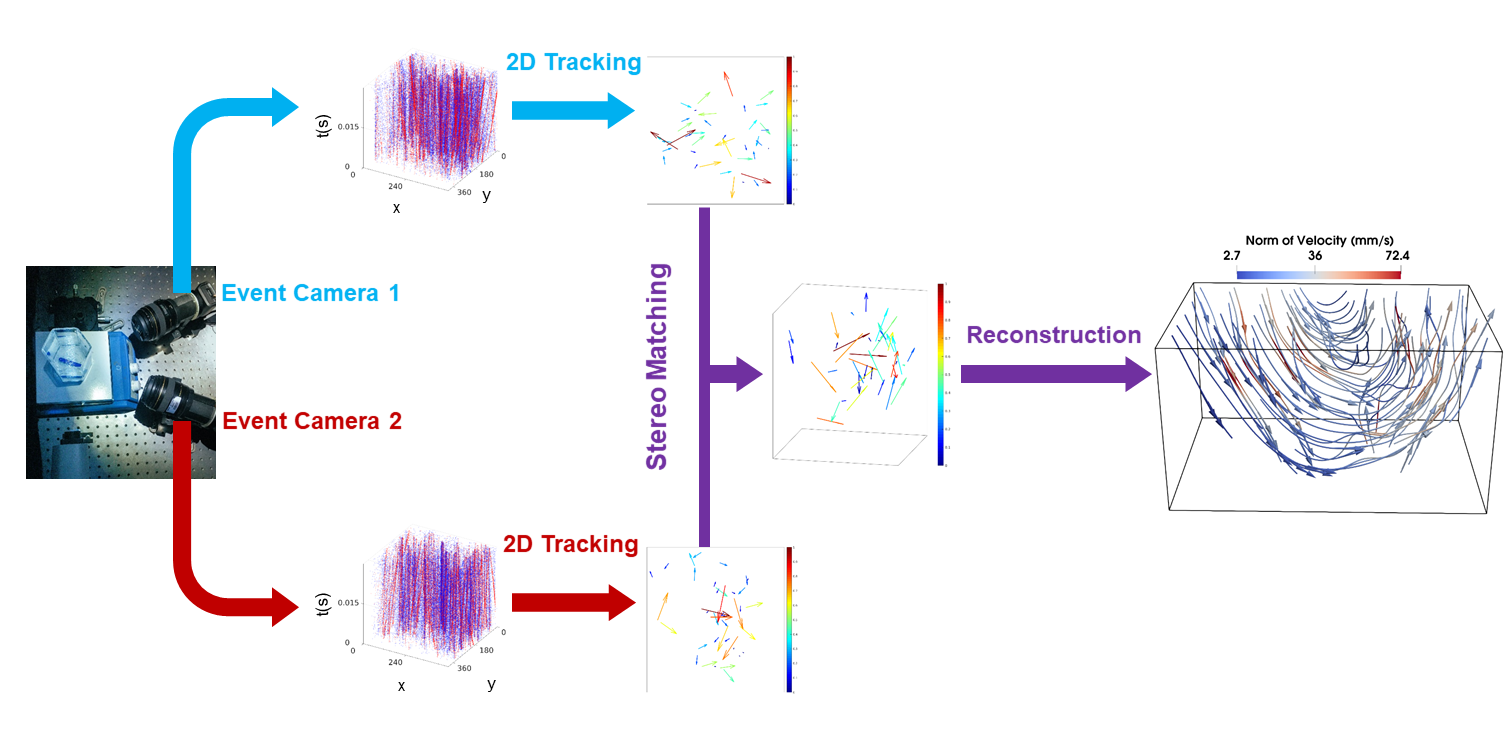
Overview of the architecture of our framework.
Abstract
Existing Particle Imaging Velocimetry techniques require the use of high-speed cameras to reconstruct time-resolved fluid flows. These cameras provide high-resolution images at high frame rates, which generates bandwidth and memory issues. By capturing only changes in the brightness with a very low latency and at low data rate, event-based cameras have the ability to tackle such issues. In this paper, we present a new framework that retrieves dense 3D measurements of the fluid velocity field using a pair of event-based cameras. First, we track particles inside the two event sequences in order to estimate their 2D velocity in the two sequences of images. A stereo-matching step is then performed to retrieve their 3D positions. These intermediate outputs are incorporated into an optimization framework that also includes physically plausible regularizers, in order to retrieve the 3D velocity field. Extensive experiments on both simulated and real data demonstrate the efficacy of our approach.Experimental Setup
Our experimental setup used for the event-based fuild imaging.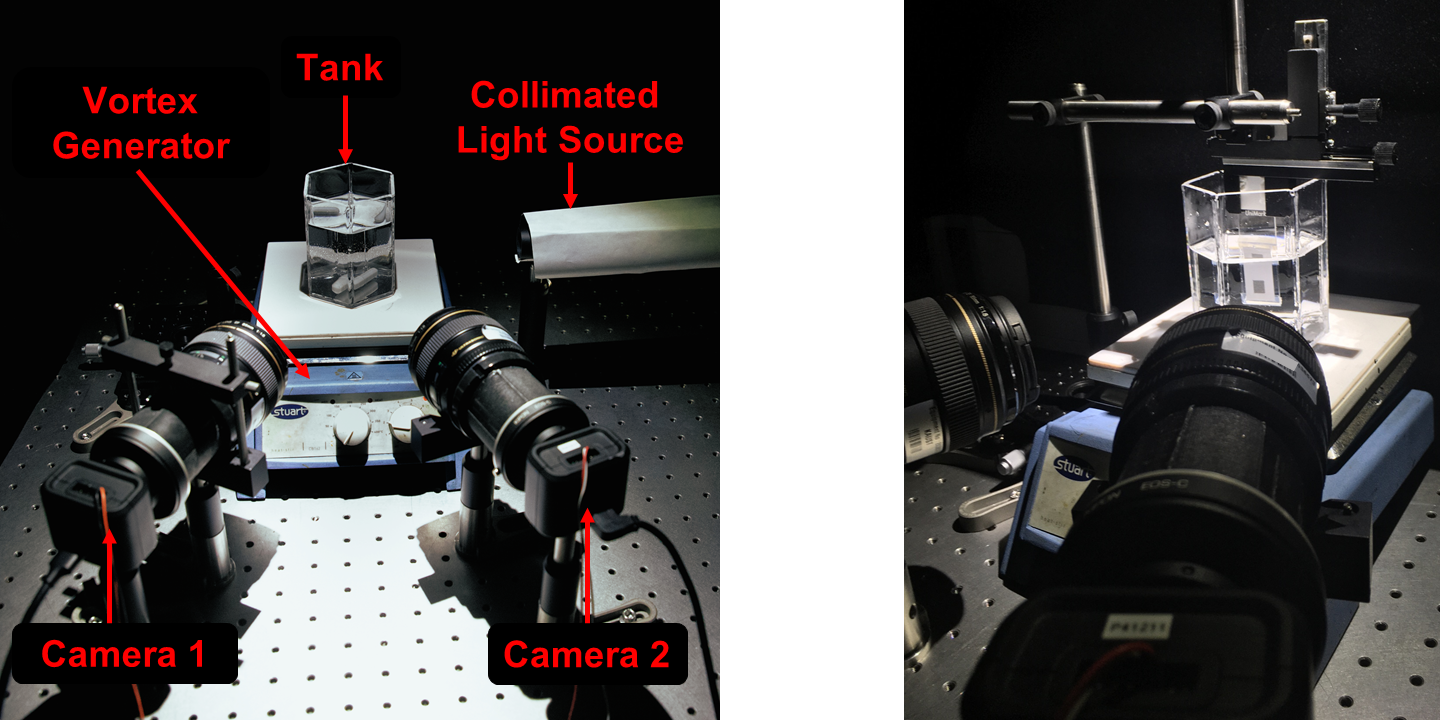
Main Results
Stiring speed set to 2.5 for the magnetic stirring rod(Model: Stuart CB162)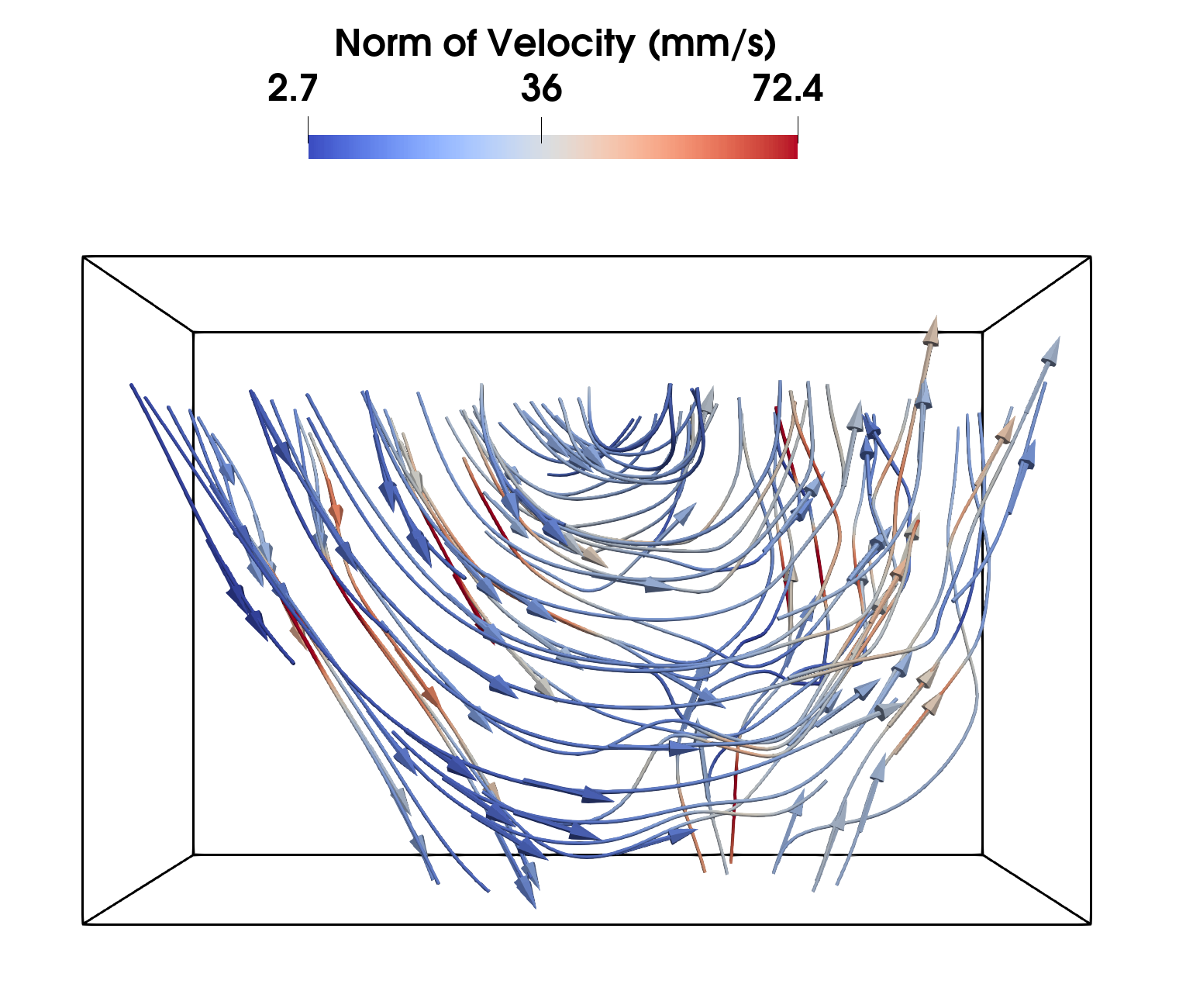
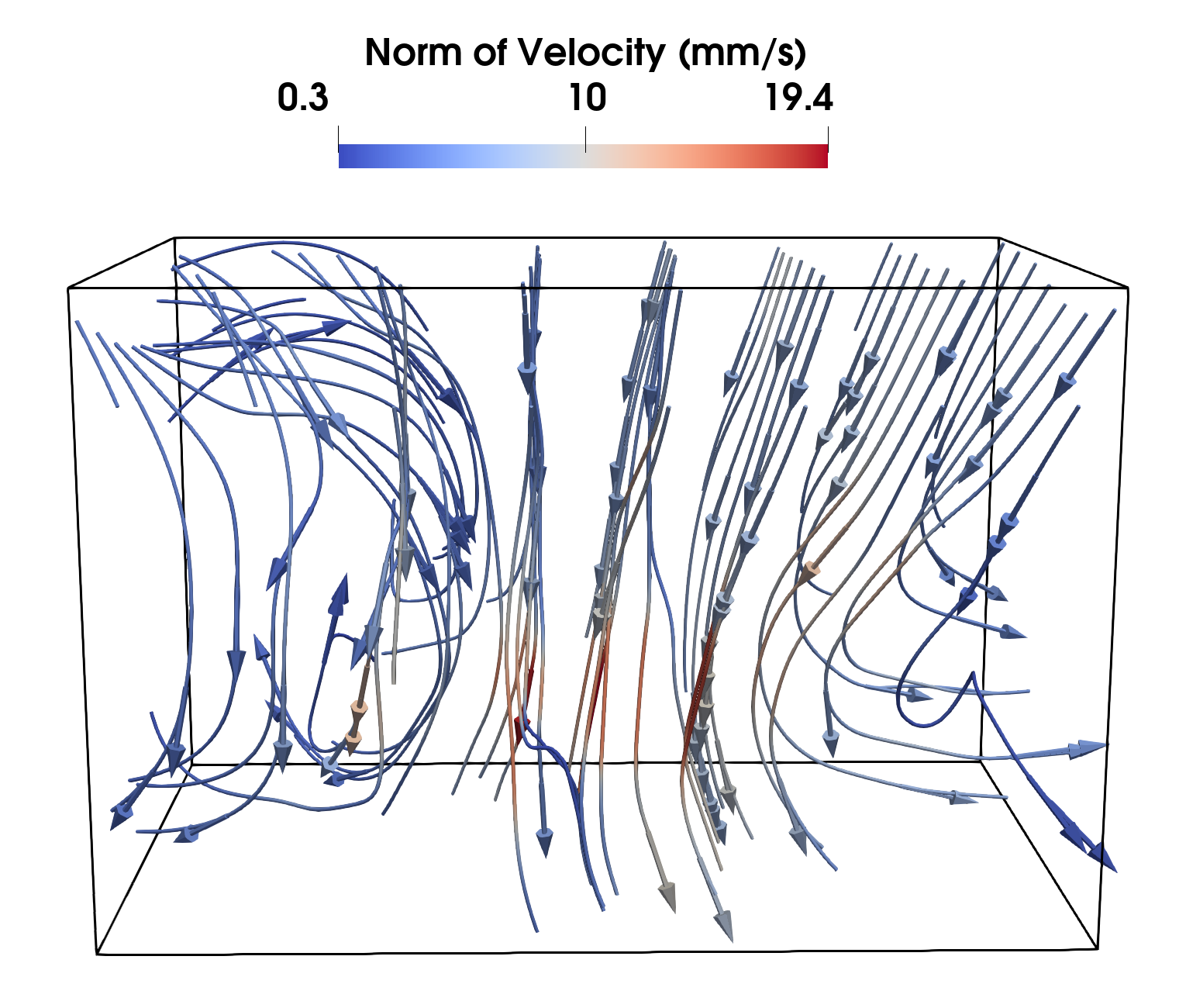
Fast vertical injection
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by King Abdullah University of Science and Technology as part of VCC Center Competitive Funding. The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments. We thank Hadi Amata for his help in the design of the hexagonal tank and the camera extension tubes. We also thank Congli Wang for helping in the use of the event cameras.Paper, code and video
Paper [Wang2020StereoEventPTV.pdf (~6.5MB)]
Supplement [Wang2020StereoEventPTV-supp.pdf (~11.4MB)]
All dataset and results [dataset]
Source code [Source code]
