A Statistical Model for OCT Image Denoising
Muxingzi Li, Ramzi Idoughi, Biswarup Choudhury,
Wolfgang Heidrich
Accepted to Biomedical Optics Express
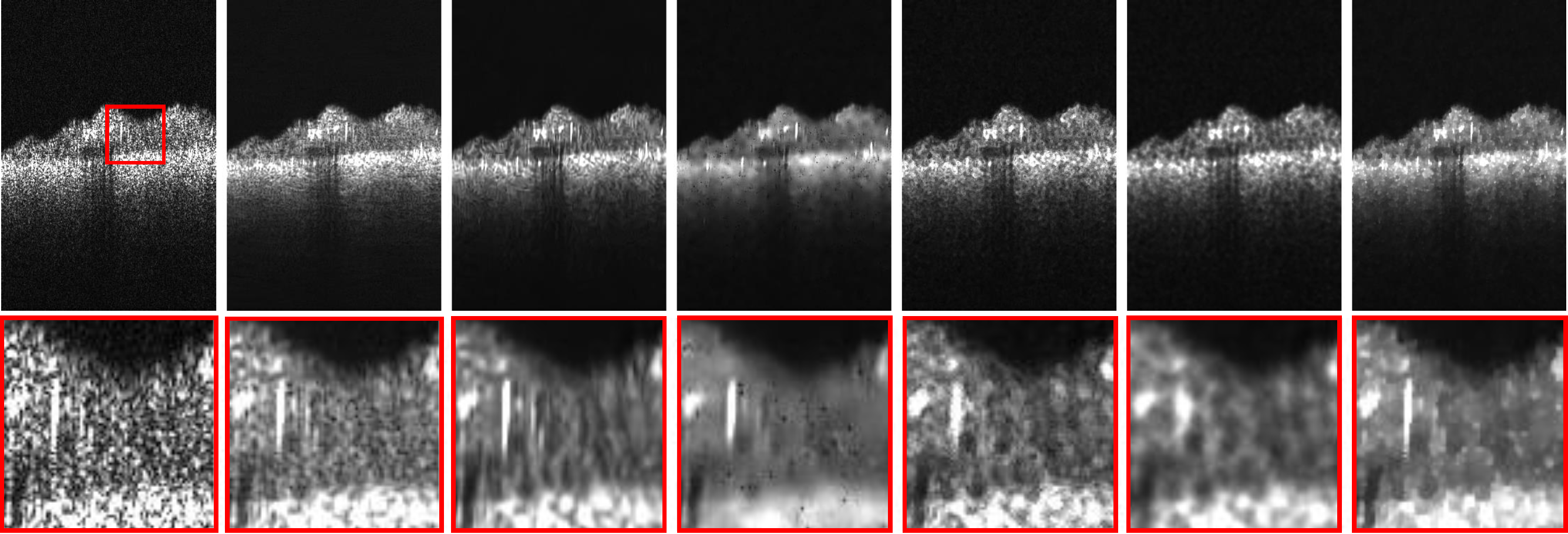
Denoising results of one B-scan with different denoising methods. The sample is a biofilm grown underwater on a membrane. From left to right: Original noisy B-scan, denoised with MSBTD, log BM3D, K-SVD, general Bayesian, TGV decomposition, proposed method. The proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance in noise reduction while yielding clear edges.
Abstract
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive technique with a large array of applications in clinical imaging and biological tissue visualization. However, the presence of speckle noise affects the analysis of OCT images and their diagnostic utility. In this article, we introduce a new OCT denoising algorithm. The proposed method is founded on a numerical optimization framework based on maximum-a-posteriori estimate of the noise-free OCT image. It combines a novel speckle noise model, derived from local statistics of empirical spectral domain OCT (SD-OCT) data, with a Huber variant of total variation regularization for edge preservation. The proposed approach exhibits satisfying results in terms of speckle noise reduction as well as edge preservation, at reduced computational cost.Paper
Paper [BOE2017_OCT_Denoising.pdf (5.9MB)]
Code & Data [Github Repository]
BitTeX @Article{Li:17,
author = {Muxingzi Li and Ramzi Idoughi and Biswarup Choudhury and Wolfgang Heidrich},
journal = {Biomed. Opt. Express},
keywords = {Noise in imaging systems; Speckle; Statistical optics; Image enhancement;
Optical coherence tomography},
number = {9},
pages = {3903--3917},
publisher = {OSA},
title = {Statistical model for OCT image denoising},
volume = {8},
month = {Sep},
year = {2017},
url = {http://www.osapublishing.org/boe/abstract.cfm?URI=boe-8-9-3903},
doi = {10.1364/BOE.8.003903},
}
